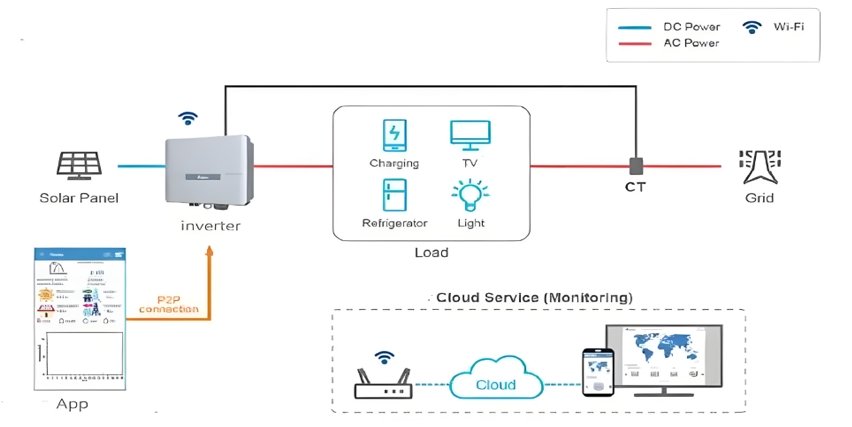
Inverters are crucial components in energy systems, converting direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) for household appliances. Understanding inverter voltage—both input and output—is key to selecting the right inverter for your system. This guide explains the different types of inverter voltages and how to choose the right one for your home.
Inverter voltage plays a vital role in determining the efficiency and compatibility of your energy system. Let’s break down input and output voltages and how to select the right inverter voltage for your home.
Curious about inverter voltages and how they impact your power system? Let’s dive in.
Входное напряжение
Сайт input voltage1 of an inverter refers to the voltage level at which it receives energy. This is typically DC (direct current) power coming from a battery or solar panel system. Inverters are designed to accept a range of input voltages based on the configuration of your energy setup.
Understanding input voltage is critical for ensuring that the inverter is compatible with your power source, whether it's a battery bank, solar array, or grid-connected system.
1. Common Input Voltage Ranges
- 12V: Small inverters designed for low-power applications such as small solar setups or RV systems.
- 24V: Common in medium-sized residential or commercial applications. Offers a good balance between power capacity and system efficiency.
- 48V: Often used for large-scale systems, as it can support higher power outputs while reducing energy losses and system costs.
2. Choosing the Right Input Voltage
The input voltage should match the voltage of the battery bank or solar panel array used in your system. For example, if you have a 12V battery bank, you need an inverter that can accept 12V input. For a larger solar system or industrial setup, a 48V inverter may be more appropriate.
| Входное напряжение | Common Use |
|---|---|
| 12V | Small-scale systems (e.g., RVs, off-grid homes) |
| 24V | Medium-scale residential or commercial setups |
| 48V | Large-scale systems or industrial applications |
Output Voltage
Сайт output voltage2 of an inverter refers to the AC (alternating current) voltage supplied to your appliances or the grid. Most household appliances require AC power, typically at standard voltage levels, depending on your country or region.
Choosing the correct output voltage ensures that your inverter is compatible with the voltage standards of your home or business appliances.
1. Common Output Voltages
- 120V: Used primarily in North America for residential applications.
- 220V: Common in Europe, Asia, and many other parts of the world.
- Other Configurations: Some commercial or industrial inverters may offer higher voltage outputs, such as 400V or 480V.
2. Matching Inverter Output to Appliance Requirements
The output voltage must match the standard voltage of the appliances or systems you intend to power. For instance, in a home in the United States, most appliances run on 120V AC, so you would need an inverter that supplies 120V output. In Europe, 220V AC is the standard, so you would choose an inverter that outputs 220V AC.
| Output Voltage | Common Use |
|---|---|
| 120V | Common in North America for household appliances |
| 220V | Standard in Europe, Asia, and other regions |
| Higher Voltages | Commercial and industrial systems, special appliances |
What Voltage Inverter Should You Choose for Your Home?
Choosing the right voltage inverter for your home depends on several factors, including the local voltage standards and the energy system you're using (solar, battery storage, grid, etc.).
What voltage inverter you should choose for your home3 depends on your region’s standards, appliance load, and energy storage system.
1. Voltage Standards by Region
- In North America: Homes typically use 120V AC for appliances, and 12V or 24V DC for small off-grid systems, though larger setups might use 48V DC.
- In Europe and Asia: 220V AC is the standard output voltage for most homes, and systems generally operate with 24V or 48V DC input.
2. Sizing the Inverter for Home Use
The size of the inverter (in watts) you choose for your home should be based on the total wattage of appliances you plan to power. For example, if your home’s total appliance load is around 3000W, you would need an inverter that can handle that output. It's also recommended to choose an inverter with a slightly higher wattage rating to allow for peak loads and surges, particularly when appliances with high starting wattage (like refrigerators or air conditioners) are turned on.
For typical residential solar systems, a 24V или 48V inverter is often preferred for higher efficiency and to minimize energy losses. The higher the voltage, the less current is required to deliver the same amount of power, making the system more efficient.
3. Compatibility with Battery and Solar Panel Systems
If you’re using a solar power system or battery backup, ensure that the inverter’s input voltage matches your solar array’s output voltage. Most residential solar systems use either 24V или 48V batteries, so choose an inverter that supports those voltages. For example, a 48 В инвертор can support a larger load, and it is more efficient in larger systems than a 12V inverter.
| Region | Output Voltage | Common Inverter Input Voltage (for home systems) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 120V AC | 12V, 24V, or 48V DC |
| Europe and Asia | 220V AC | 24V or 48V DC |
Заключение
Choosing the right inverter voltage is essential for the efficiency and compatibility of your energy system. The input voltage should match your energy source (battery or solar panels), while the output voltage should correspond to the voltage standards of your region and the appliances you wish to power. Understanding these voltage requirements will ensure your inverter operates optimally and provides reliable power for your home or business.
Сноска:
-
Эта ссылка объясняет input voltage, its significance in inverter compatibility with power sources like batteries and solar systems, and how to choose the right range. ↩
-
Эта ссылка объясняет output voltage, its importance in ensuring compatibility between inverters and household or commercial appliances based on regional voltage standards. ↩
-
Эта ссылка объясняет what voltage inverter you should choose for your home, considering factors like regional voltage standards, appliance needs, and system compatibility. ↩